Medical science continues to make great progress in diagnosing
illnesses and treating them. Devices of many types allow doctors to see inside
the body to diagnose a variety of conditions. Other types of medical devices
that are used or implanted inside the body provide relief from many painful
conditions. However, no matter how far medical science has progressed, there
are still risks and benefits that people need to consider before undergoing
even the most routine procedure involving a medical device.
Here are a few common devices and procedures, as well as some
injuries and issues that have been associated with them.
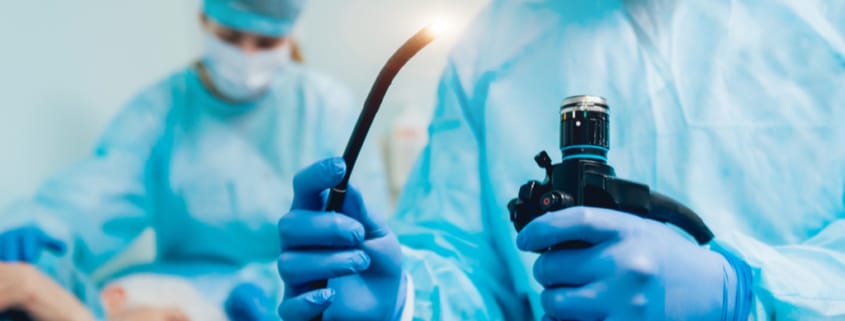
Medical Scopes
Each year, millions of people in the U.S. have a procedure with
a medical scope of some type. In these procedures, a doctor places an
instrument called an endoscope inside the body to examine the esophagus,
stomach, bile ducts, colon, lungs, bladder, or other organs. After each
procedure these devices are cleaned and re-used on another patient. Duodenoscopes,
which are used to diagnose and treat stomach and other GI tract conditions,
have been of particular concern.
Since 2013, at least 35 people have died from after having a
procedure that used a duodenoscope. The problem is that the design of the scope
makes cleaning
it extremely difficult, so even if the scope is cleaned according to the
manufacturer’s instructions, bacteria can still be trapped inside the scope and
transferred to another patient. A paper
published in April 2018 showed that 71 percent of scopes tested at three major
U.S. hospital were contaminated with bacteria.
In 2015 the FDA
directed three duodenoscope manufacturers (Olympus, Fujifilm, and Pentax) to
study this issue. Interim
results of these studies released in December 2018 showed that up to three
percent of samples were contaminated with “low-concern” organisms, and up to three
percent were contaminated with organisms of high concern. Sampling is
continuing.
One manufacturer, Olympus, pled guilty
in December 2018 to charges of failing to file reports about infections stemming
from its scopes. The company agreed to
pay $85 million to resolve the charges. Additionally, the company settled lawsuits
with two women whose husbands died after undergoing a procedure with the scope
and becoming infected with a “superbug” bacteria resistant to most antibiotics.
Other types of scopes are similarly difficult to clean. Bronchoscopes,
which are used to look inside the lungs, have also been found to be contaminated,
even after cleaning, and have likewise been linked to “superbug” infections.
Bone Cement
There are over a million joint replacements performed each
year in the U.S. In many of these procedures, the surgeon uses bone cement.
Bone cement doesn’t actually “glue” the joint into place; it fills the space
between the artificial joint and the bone to keep the joint in place. The use
of bone cement in joint replacements is not without complications, however. The
bone cement can break loose, which can cause pain and affect movement. It can
also leak
into the body.
The most serious problem is bone cement implantation
syndrome (BCIS).
Fortunately, this complication is rare, but when it happens, it causes the
cardiovascular system to collapse and can cause death,
often during the procedure. BCIS has
been reported with knee,
shoulder, and hip
replacements. One study
from the UK reported 41 deaths linked to the use of cement in hip replacement.
BCIS has also been reported in patients undergoing spinal
surgery. As early as 2002, the FDA sent a warning
about a bone cement that was being used to treat spinal fractures and had been
linked to serious complications, including blood clots in the lungs, cardiac
failure, and death.
In 2011 the government filed charges against a company
called Synthes, a manufacturer of bone cement. The company had been testing a
cement that had not been approved by the FDA for use in spinal surgeries. Five
patients who received the cement had died during surgery after the company ignored
reports that the cement could have fatal consequences. Because the company had
not been conducting a clinical trial, patients weren’t advised of the risks and
given a chance to decide if they wanted to receive the bone cement. Four
Synthes executives were also charged, pled guilty and sentenced to time in
jail.
Pelvic Mesh
Pelvic mesh is a relatively recent product that was
initially marketed in the 1990s to treat stress urinary incontinence in women.
After the success of that product, it started being used for pelvic organ
prolapse. However, the use of the mesh for pelvic organ prolapse has been
associated with complications
including pain, infection, bleeding, mesh erosion, urinary problems, and
perforation of organs, and has prompted tens of thousands of lawsuits.
The FDA received over 10,000 reports of serious
injuries from pelvic (transvaginal) mesh that occurred from January 2008 to
October 2018, including 77 deaths. Previously, in 2011, the FDA had issued a
warning, and in 2016 they classified it as a high-risk device.
Earlier this year, a woman was awarded $41
million in a verdict against one of the manufacturers of pelvic mesh,
Johnson & Johnson. Altogether, more than 100,000
women are suing manufacturers of pelvic mesh due to the complications they have
experienced. Some women describe continuous pain due to the plastic of the mesh
perforating the vaginal wall.
This is another instance of the product being marketed and
used without the benefit of long-term study,
to the detriment of thousands of women. Transvaginal mesh and is banned
in the UK, Australia and New Zealand. On February 12, 2019, an FDA
panel met to discuss the future of transvaginal mesh in the U.S. The panel
decided that rather than pulling the mesh off the market, they would like more
long-term studies.
What to Do If You
Need a Procedure or Medical Device
If you are faced with needing a medical procedure or device,
how can you weigh the risks and benefits? You need to be fully aware of whether
the device has been studied in clinical trials and has been approved by the
FDA. Even if a device has been approved , such as a duodenoscope, you need to
know if there are other issues, such as infection risk, associated with its
use.
Doing an internet search on the device or procedure may help
answer questions such as:
- What is the history of the procedure/device?
- Has the device been approved by the FDA?
- What are the risks and benefits?
- What complications have been reported?
- Are there ongoing lawsuits associated with the
device?
- What are the alternatives?
You should also carefully read the consent document for the
procedure, as it should list the potential risks and complications.
Speak with your healthcare providers also. What is their
experience with the procedure/device? How many times have they done the
procedure? What are the most common
complications? Before making a decision, you may also want to speak with other
patients who have had the procedure.
The bottom line is that you should arm yourself with as much
knowledge as you can before undergoing a procedure so you know the risks and
benefits and can make an informed decision.